8/28/2023
Global radiation benchmark - Meteonorm is among the leaders
In the framework of IEA PVPS Task 16, a benchmark of different satellite and model-based radiation databases was carried out. The Meteonorm time series show good quality and are among the top performers.
As part of the international cooperation in IEA PVPS Task 16, a new benchmark of satellite and model based data sources was carried out. Meteotest also participated with the product Meteonorm time series.
The time series of the participants were compared with radiation data from ground measuring stations and statistically evaluated. The comparisons show large differences between the data sources, global and direct radiation and the continents.
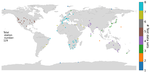
Figure: Location and number of test data sets per reference station. Stations that were used by one or two providers for post-processing are marked with crosses (source).
In Europe, the models are the best. The satellite-based Meteonorm data performs very well there. Meteotest's method corrects the satellite data regionally to the ground data. The better these are, the better the radiation data from Meteonorm. In places with little or less good radiation data, e.g. in south-eastern Africa, the differences are bigger.

The table shows the deviation (relative Mean Bias Deviation, rMDB) of the different radiation data at the investigated locations. In addition, the mean of the MBD, the standard deviation, the mean of the absolute values and the standard deviation of the absolute values are listed. The Meteonorm time series are listed as METEOTEST (source).
Overall, Meteonorm ranks second in the benchmark, surpassed only by an expensive high-end product. The Meteonorm database is regularly updated and the method improved. The Meteonorm data is available worldwide in the Meteonorm desktop software, as a time series single order or via API.

Your contact
Jan Remund
Head of Energy & Climate
| |